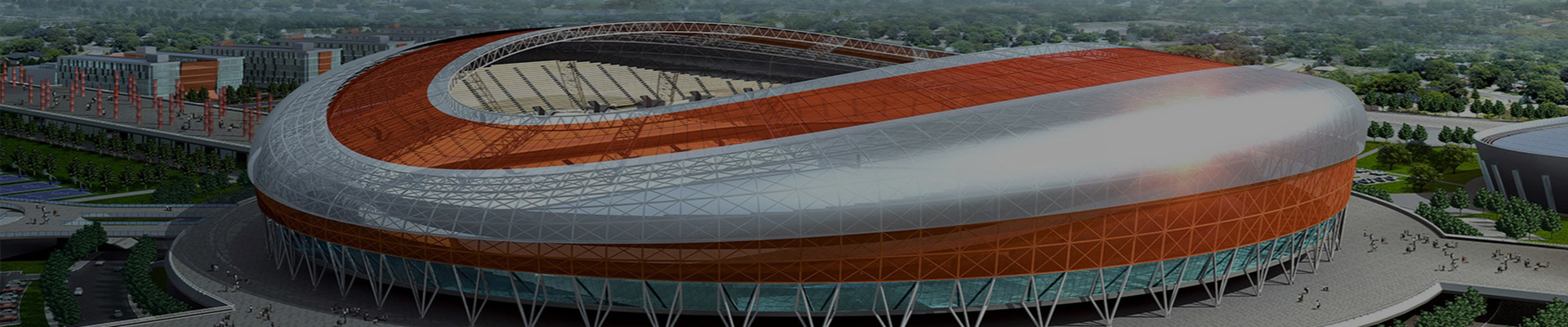
What's the Difference Between PVDF and Other Color Plate Coatings?
What’s the difference between PVDF and other color plate coatings? In the color coated steel industry, coating performance plays a decisive role in durability, appearance, and long-term cost. Among various coating options, PVDF coating is widely regarded as a premium choice. Understanding how PVDF differs from other common color plate coatings helps architects, builders, and manufacturers select the most suitable solution for different applications.

1. What Is PVDF Coating?
PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) is a high-performance fluorocarbon resin coating commonly used on color coated steel plates. It is known for its exceptional resistance to weathering, ultraviolet radiation, chemicals, and corrosion. PVDF coatings are typically applied in a two-coat or three-coat system and are widely used in high-end architectural and exterior applications.
2. Comparison with Polyester (PE) Coatings
Polyester (PE) coatings are the most common and cost-effective option for color plates. They offer good color variety and basic weather resistance, making them suitable for general construction and indoor or short-term outdoor use.
Compared with PE coatings, PVDF provides significantly better UV resistance, color stability, and durability. While PE coatings may fade or chalk over time, PVDF coatings maintain their appearance for decades, especially in harsh outdoor environments.
3. Comparison with SMP (Silicon-Modified Polyester) Coatings
SMP coatings improve upon standard polyester by adding silicon, which enhances hardness and weather resistance. SMP color plates perform better than PE in terms of scratch resistance and durability.
However, PVDF coatings still outperform SMP coatings in long-term color retention and chemical resistance. PVDF is more flexible and less prone to cracking, making it a preferred choice for complex forming and extreme climate conditions.
4. Comparison with HDP (High-Durability Polyester) Coatings
HDP coatings are designed to bridge the gap between SMP and PVDF by offering enhanced weather resistance and longer service life than standard polyester systems.
While HDP coatings are a strong mid-range option, PVDF remains superior in environments with intense UV exposure, coastal areas, or industrial pollution. PVDF’s fluorocarbon structure provides unmatched resistance to fading and corrosion.
5. Durability and Service Life Differences
One of the most significant differences between PVDF and other color plate coatings is service life. PVDF-coated color plates can maintain performance and appearance for 20–30 years or more with minimal maintenance. In contrast, PE, SMP, and HDP coatings generally have shorter service lives depending on environmental conditions.
6. Cost and Application Considerations
PVDF coatings are more expensive than other coating systems due to higher material and processing costs. However, their long lifespan and reduced maintenance often result in lower life-cycle costs. For landmark buildings, commercial façades, airports, and high-end industrial projects, PVDF-coated color plates provide long-term value and reliability.

Conclusion
The difference between PVDF and other color plate coatings lies mainly in performance, durability, and long-term value. While polyester, SMP, and HDP coatings serve well in standard applications, PVDF stands out for superior weather resistance, color stability, and extended service life. Choosing the right coating depends on project requirements, environmental exposure, and budget, but for demanding applications, PVDF remains the premium solution.
-
 2025-04-01
2025-04-01How can color-coated plate wholesalers seize the opportunity of new infrastructure construction and expand their market share?
-
 2026-01-17
2026-01-17How Does HDP Coating Extend the Life of Color Steel?
-
 2025-04-01
2025-04-01Color-coated sheet wholesalers face compliance challenges under policy and regulatory adjustments
-
 2025-04-01
2025-04-01Color matching and architectural design: the artistic beauty of the color card comparison industry of color steel coils